App Optimization Suggestions
You should stay with Unity LTS (Long-term support) versions only while upgrading Unity Editor versions.
Utilize profiling to identify the sections within the app where heavy CPU and memory usage occur. Check out our guides to perform profiling below -
Remove unused assets from the project. Please go through the build report and identify the assets that use up most of the size. The build report inspector tool can be utilized. https://github.com/Unity-Technologies/BuildReportInspector/tree/master
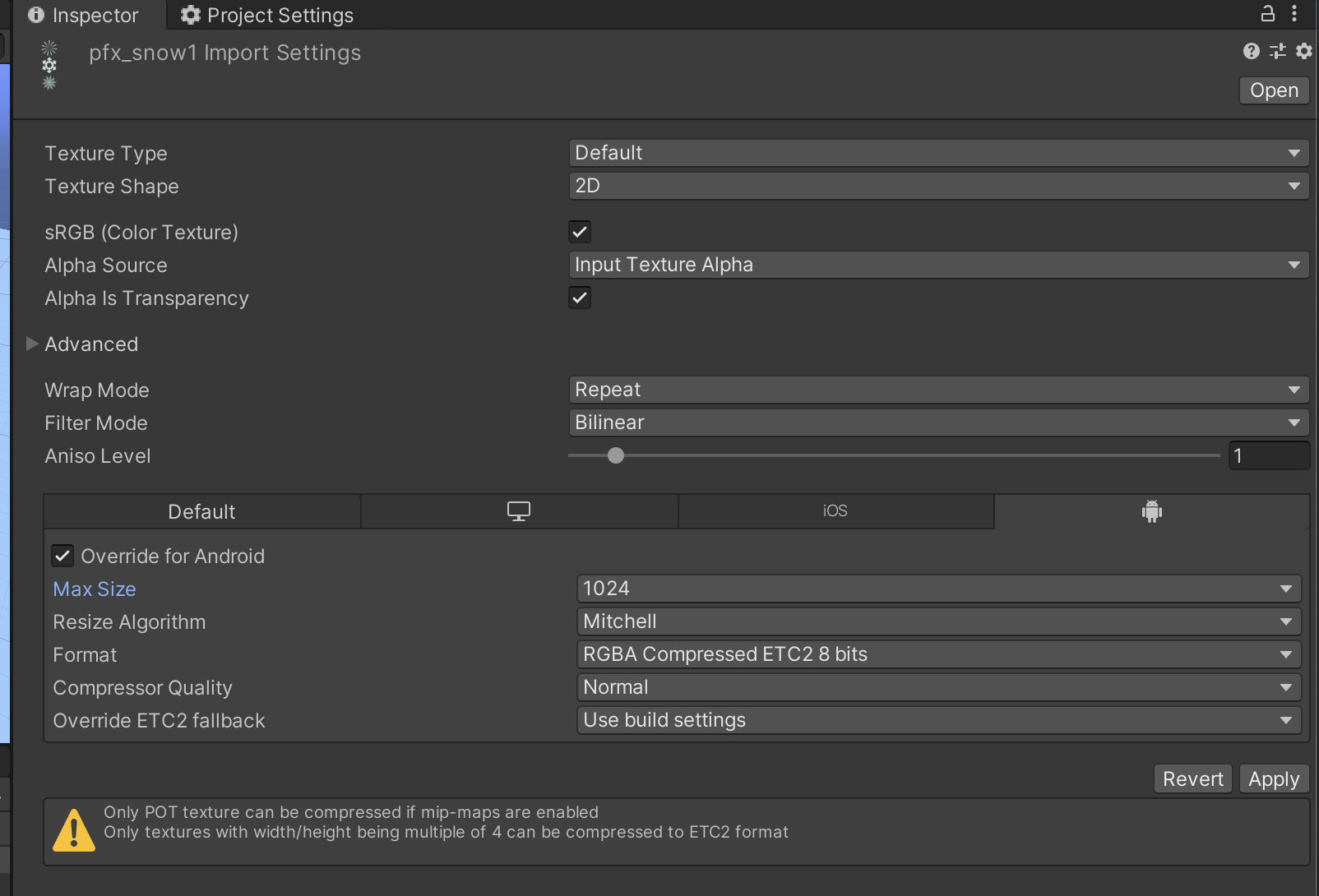
Use unity compression for sprites, textures, audios and animation files. The dimensions of the texture should be in power of two or should be in multiples of 4 for compression to be executed.
- Optimize Text with TextMesh Pro instead of default Unity Texts.
- Remove all unused lifecycle methods like Awake, Start, OnEnable, Update etc.

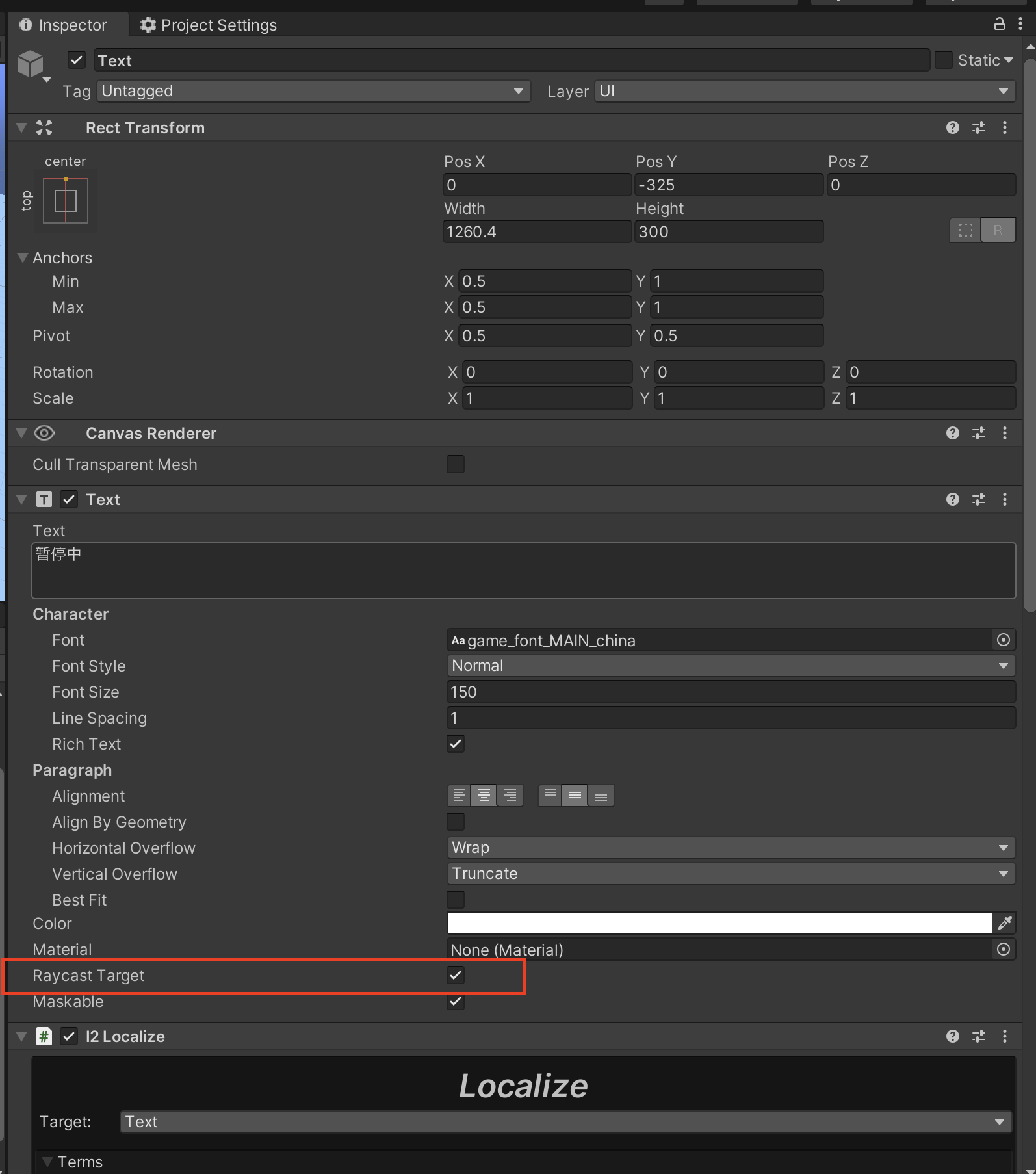
- Remove all the Raycast Target of all the game objects in which it is not used. For example a text on button doesn't require this. This is turned on by default and continuously check for raycast like in an update function.
- Remove all Debug.Log method calls used in the project. Each call uses certain amount of memory to execute and print the logs.
- Remove all the warnings in project in Unity Editor.
- Try to use multiple canvases. If all the UI elements are in a single canvas, one small change results in the refresh rendering of whole canvas.
- Avoid using Camera.main. Instead cache the main camera once and reuse this. Using Camera.main slows down the game.
- Use string builder instead of string concatenation.
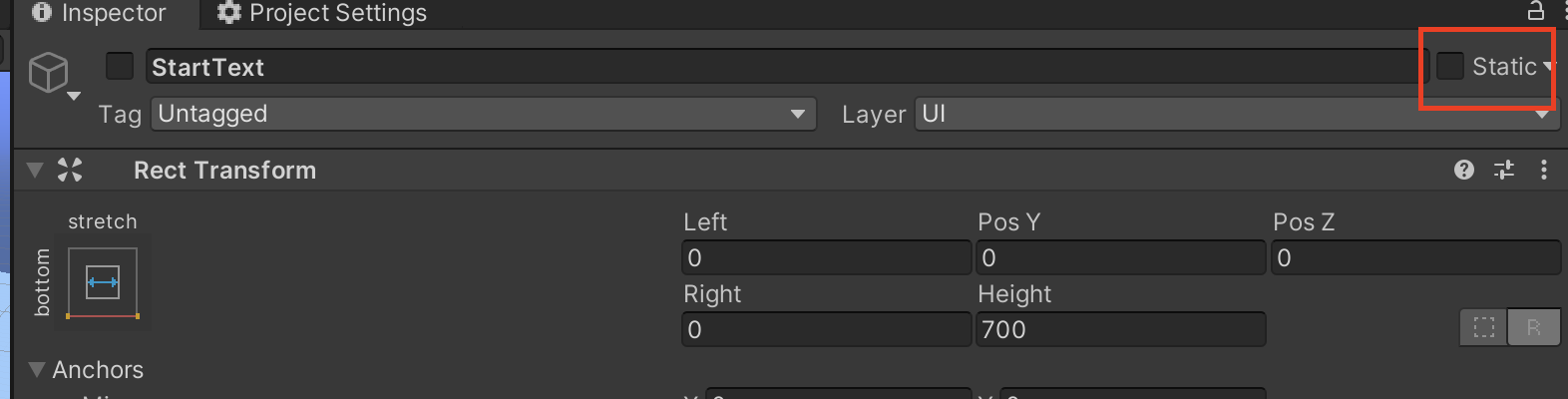
- Set gameobjects to static, that will not move in the game.
- During OnApplicationPause, ensure that all actions taken are necessary. Consider saving the user’s state in local device memory to minimize processing. Also, evaluate whether certain actions can be executed outside the pause period.
- Streamline OnApplicationPause and OnApplicationFocus: Keep these callbacks lightweight to avoid excessive processing that can lead to ANRs.
- Avoid Synchronous Operations: Do not perform blocking I/O or network requests within these callbacks; instead, handle such tasks asynchronously.
- Identify and categorize devices with lower performance or known stability issues to apply targeted optimizations and reduce ANRs for affected users.
- Initialize third-party SDKs sequentially rather than in parallel to prevent resource contention and reduce startup time issues.
- Use Animator.StringToHash for triggers and properties to improve performance by storing computed hash values as static readonly fields.
- Example Optimization:This ensures that hash values are computed only once at runtime, reducing unnecessary processing overhead.
private static readonly int AttackTrigger = Animator.StringToHash("attack");
...
anim.SetTrigger(AttackTrigger);
...
- Example Optimization:
- Use Shader.PropertyToID for shader properties to avoid repeated string lookups and improve rendering performance.
- Example Optimization:
private static readonly int ColourProperty = Shader.PropertyToID("_Colour");
...
material.SetColor(ColourProperty, Color.red);
...
- Example Optimization:
- Disable Opaque Texture in the URP Asset unless required, so URP only copies the color buffer when necessary, reducing performance overhead.
- Disable Depth Texture in the URP Asset unless specifically needed (e.g., for shaders that rely on scene depth) to optimize rendering performance.
- Use object pooling
- Instead of destroying and creating game objects, re-use the objects using object pooling.
- It is very important to keep your project clean without errors, missing stuff, and unnecessary files.